This article is a translation of the German IOTA Beginner’s Guide by .

Use Cases
Zühlke: Machine-as-a-Service – IF
Industry 4.0
With the ongoing digitization of product manufacturing, we are in the midst of a significant shift in the way we manufacture products.
This transition is commonly called Industry 4.0, as it is the fourth phase of the revolution in the history of manufacturing. Industrial revolutions can be roughly described in four phases. The first phase is referred to as mechanization by water and steam power. The second phase was the introduction of electric mass production and assembly lines. The third and current phase is characterized by the automation and networking of production facilities through computers.
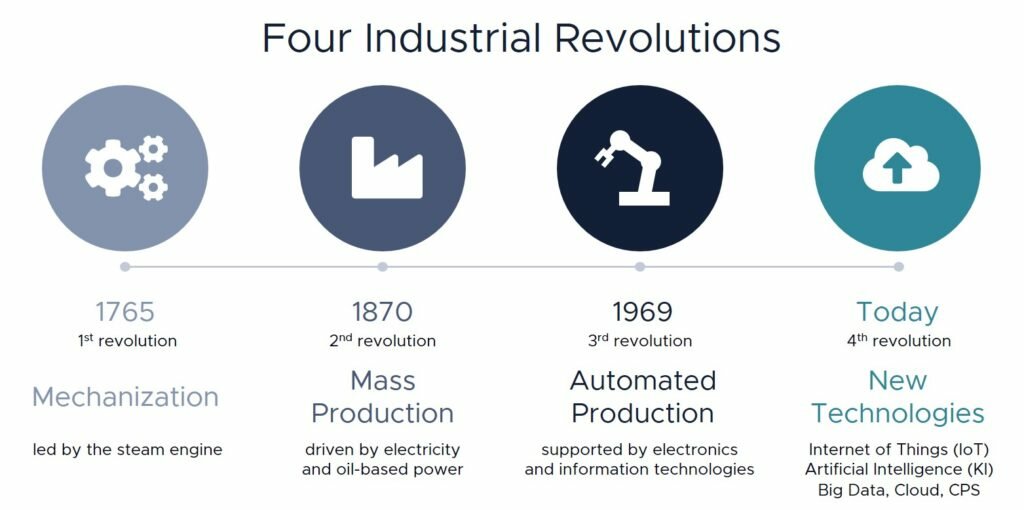
The fourth phase, called Industry 4.0, optimizes the computerization of the third phase. Manufacturing plants are interconnected and communicate with each other to ultimately make decisions without human intervention. A combination of cyber-physical systems, the Internet of Things and the Internet of Systems make Industry 4.0 and the Smart Factory possible.
By supporting smart machines, with access to more and more data, factories become more efficient, more productive and less wasteful. Ultimately, it is the network of these machines that are digitally connected, providing data and sharing information that is the true potential of Industry 4.0. The big challenge for companies is to recognize and exploit the emerging opportunities of connected smart manufacturing plants.
What about IOTA?
The manufacturing industry is facing the fourth industrial revolution, characterized by Industrial IoT. Smart factories will leverage massive amounts of data from manufacturing processes to improve efficiency, increase production, reduce waste, and build trust. IOTA technology will enable data-driven infrastructure and new business models across industries, creating a new ecosystem.
This new machine economy will be a win-win-win for consumers, manufacturers and businesses. The Distributed IOTA ledger consists of a highly scalable and secure communication and transaction protocol with no fees. This makes it the ideal solution for M2M communications, payments, and storage of immutable data needed in the smart factories of today and the future.
Data integrity is a key aspect of Industrial IoT
Due to the ever-increasing connectivity between internal and external cyber-physical systems of smart factories, security is of utmost importance. Data integrity is a critical component of security. The immutability of data creates trust among business partners.
Tamper-proof audit trail
Internal testing procedures are continuously applied for stress testing and quality analysis of the components to be manufactured. The large amounts of data generated must be securely stored and immediately available. In an IOTA-enabled smart factory, tests are configured to log all commands and store them securely with periodic data logging. The data can then be hashed and logged to a database. Only the hash is stored in the tangle, creating a secure and tamper-proof audit trail.
Digital twins to improve a process, product or service.
A digital twin is a virtual model of the manufactured product based on trusted data to analyze and simulate real-world conditions, respond to changes, improve operations and add value.
Encrypted access management
The integrated dashboard provides authorized users with a complete view of the machine audit trail. This includes automated integrity checks for data and the ability to remotely control the machine. When finished products leave the factory, they seamlessly become part of the smart supply chain. All stakeholders involved in the supply chain can access relevant information based on the digital twin concept. Internal and external stakeholders can independently review data stored on the IOTA Tangle. IOTA also provides the ability to encrypt data with authenticated access management.
Rent or buy production capacity as a service
The machines used in factories today can operate 24/7. Any downtime is considered a lost business opportunity. What if machine owners could rent out the production line to the highest bidder?
From the factory owner’s perspective, products from different manufacturers could eliminate production line downtime and maximize factory profits.
From the manufacturer’s point of view, there could be flexibility in responding to a product’s demand situation. In addition, many fixed costs such as a factory floor, machinery, or labor costs are eliminated. This also opens up the possibility for low-volume product manufacturing.
Conclusion
By using intelligent production systems, manufacturers can pay machine owners based on the usage of each machine. For both manufacturers and factory owners, IOTA is the ideal backbone for this process: All communication, transaction recording and payments occur automatically between the manufacturer and the machines via IOTA’s secure and tamper-proof digital ledger.
Other Industry 4.0 use cases of IOTA:
- M2M micropayments
- Reduced costs through predictive maintenance
- Increased efficiency and business opportunities through smart connected machines
- Smart supply chains
- Inventory reduction through BI analysis of data stored in the Tangle
- Improved confidence in b2b through immutable and transparent record retention
- Time and cost savings for auditing data
“The possibilities of decentralized and secure applications on the IOTA Tangle as Distributed Ledger Technology are enormous. They go much further than payment between two machines and include, for example, tamper-proof supply chain control and secure identity management, to name a few.” – Rolf Werner, former Central Europe CEO Fujitsu
Original source
https://iota-einsteiger-guide.de/industrie-4-0.html
Last Updated on 16. February 2021



